| Task: Elicit Requirements |
 |
|
Requirements elicitation for a SPL must capture anticipated variations over the foreseeable lifecycle of the SPL Clements and Northrop (2001). Its information sources are probably larger than for single-system requirements elicitation. Thus, the Elicit task is responsible for identifying domain requirements and variations in a SPL. It also reaches agreement to satisfy all stakeholders, solving conflicts that are identified. Its main inputs are the Product Map (scope of the SPL), glossary and existing assets. |
| Roles | Primary Performer: | Additional Performers: |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Mandatory:
| Optional:
|
| Outputs |
|
|
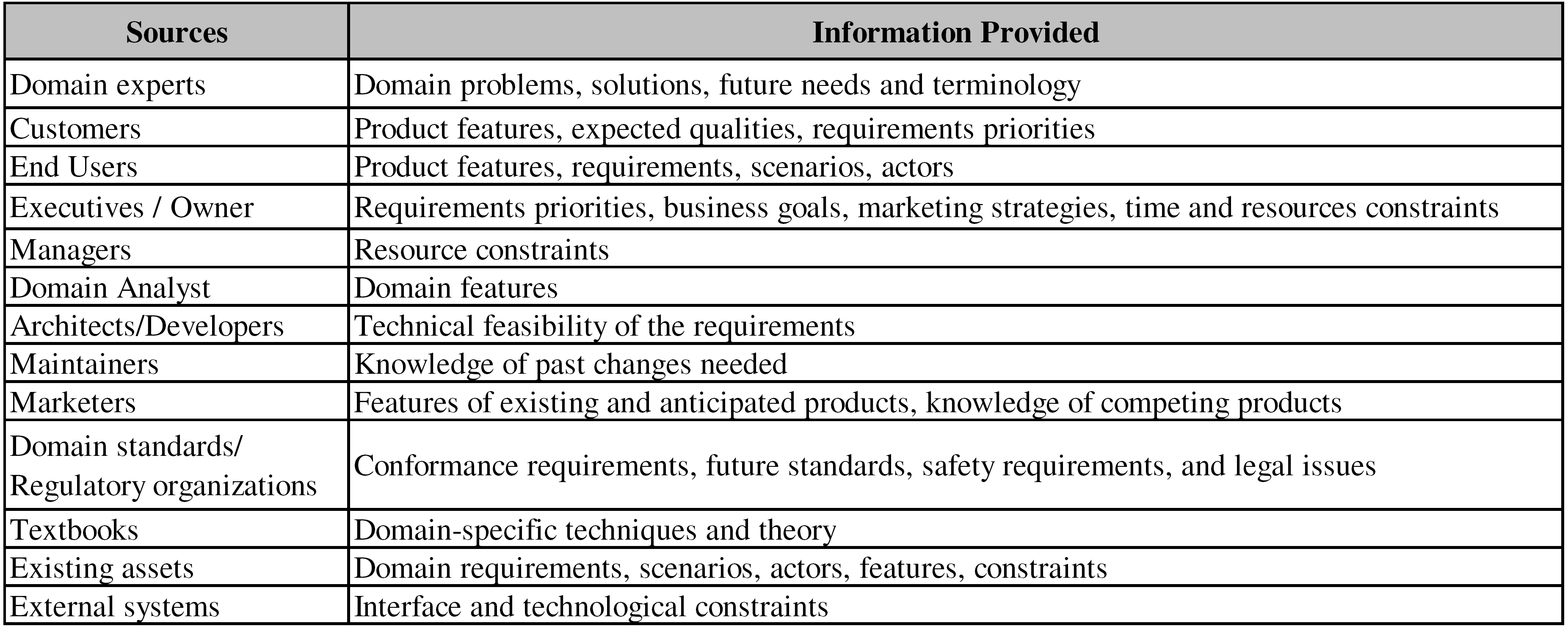
In the process initiation, this task must identify the requirements overview, defining the boundary that divides the SPL and the real world that surrounds the solution, identifying the main variations among its products. These variations must reflect value for organizations and present differential among products. Elicit is an iterative task in which new information can be added in each iteration according to its activity and work products. For example, in the Define Use Cases activity can be necessary to identify some information not yet elicited, such as actors, scenarios, pre-conditions ans their variations. It can be elicited using the existing systems and assets, interviewing potential users and domain experts. In the Define Requirements activity can be necessary to identify and negotiate priorities with different stakeholders. It can need of different stakeholders’ viewpoints, so it can result in conflicts. In this case, it is recommendable performing elicitation in a brainstorming session, in which will be performed requirements elicitation and negotiation. The identification of the SPL requirements can be performed by interview or brainstorming sessions with stakeholders that provide the necessary information. However, the potential stakeholders might be busy (e.g. expert domain with little availability), so it is recommendable that elicitation starts by other information sources, such as outputs from previous activities (e.g. product map for Model Scope activity), existing assets (e.g. user manual, available systems) and textbooks. If information cannot be found in these sources, then it is necessary to contact the stakeholders. Also, it is necessary direct and intensive contact with stakeholders when there are not existing assets and systems. Next Figure presents the systematic of the elicitation.
In this Figure the investigation in existing documentation or assets represents any information source which is not a stakeholder, for example, available DRS, textbooks, existing systems and their documentation. When elicitation is conducted in a session brainstorming, it is necessary elicit a major account of information. This session must be moderate by requirement analyst and can be conducted in more of a day. The session must be in presence of the domain analysts, domain experts and of other stakeholders of particular concern in the SPL. This brainstorming provides an opportunity to gather stakeholders together to provide input about their needs and expectations with respect to key requirements that are of particular concern to them. All participants are expected to be fully engaged and present throughout the brainstorming. Participants are encouraged to comment and ask questions at any time during the brainstorming. However, it is important to recognize that the moderator may occasionally have to cut discussions short in the interest of time or when it is clear that the discussion is not focused on the required brainstorming outcomes. Moderator also should help stakeholders create well-formed requirements. After elicitation, similar requirements are consolidated when reasonable. The vocabulary used to describe requirements varies widely, so it is necessary to search domain common terms and update them in the glossary. If common terms are not defined, different perceptions of domain concepts could cause confusion among stakeholders and lead to time-consuming discussions. Therefore, the Elicit task is concluded in each iteration with the updated glossary and raw DRS, which will be input for the following tasks. |
The elicitation strategy must be adopted according to the information source type, so its identification is essential for this task. Examples of information sources and their information provided are shown in following Table.
|